SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Osteoporosis: causes and factors of development
The reason for the development of the disease can be long-term exposure to smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal diseases and other factors. In the elderly, osteoporosis develops due to poor digestion of calcium and some nutrients.
The most common cause of osteoporosis is hormonal deficiency. In women, osteoporosis is usually noted during menopause. In this case, the disease develops not due to a lack of calcium in the body (there is enough calcium), but due to a violation of the activity of bone-forming cells. These events are caused by a violation of hormonal balance, so in this case, women should consult a gynecologist and receive hormonal therapy, if necessary.
Brittleness of bones with age is a natural physiological phenomenon. However, in some people, these processes occur rapidly. This can be caused by some factors, including:
- Female gender;
- Europoid or Mongoloid race;
- Thinness of bones;
- Old age (over 65 years);
- Predisposition to hereditary diseases;
- Vitamin D deficiency;
- Frequent use of certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids and anticonvulsants);
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Smoking;
- Excessive alcohol consumption;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Disorders of ovarian function;
- Changes in the hormonal background that occur during menopause;
- Disorders of the adrenal glands;
- Other diseases of the endocrine glands.
Age-related (senile) osteoporosis, on the other hand, develops due to calcium deficiency - when the rate of bone tissue breakdown exceeds the rate of new bone tissue formation. This form of osteoporosis is usually specific to people over the age of 70 years. According to statistics, senile osteoporosis is almost twice as common in women and is associated with menopause in more than 95% of cases.
Less than 5 percent of osteoporosis is due to other diseases or the use of certain medications. It is a form of secondary osteoporosis that develops as a result of diseases of the kidneys, endocrine glands and other diseases that lead to structural-functional diseases of bone tissue.
The idiopathic form of osteoporosis is also distinguished (mainly in the young). It is a very rare disease and its cause is currently unknown. Idiopathic osteoporosis can develop in infants, children and adolescents where all hormones are normal. In addition, such people do not have diseases that lead to the development of osteoporosis.
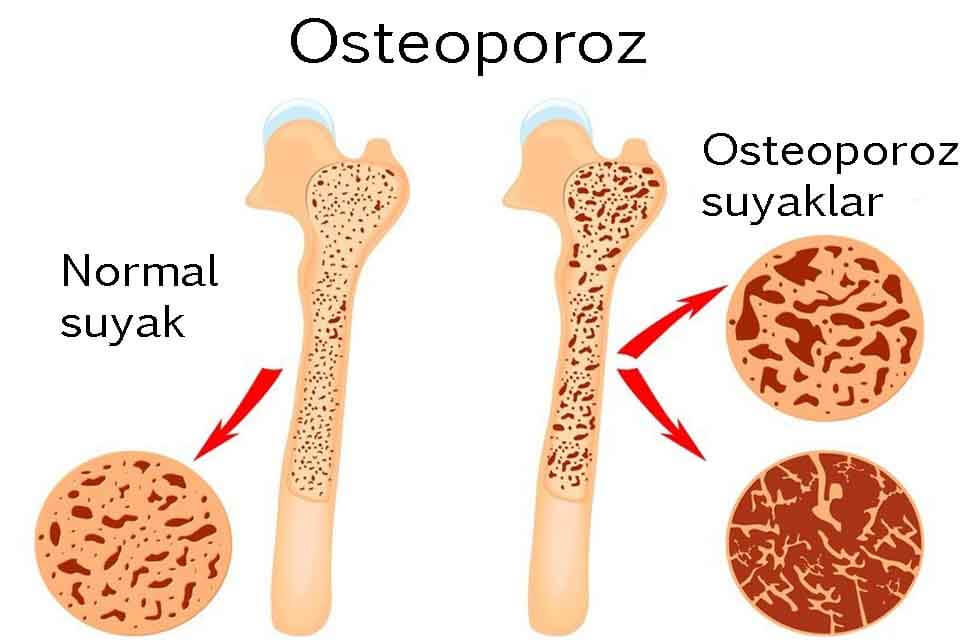 Types of disease: classification of osteoporosis
Types of disease: classification of osteoporosis
Depending on the distribution, the following are distinguished:
- Local osteoporosis;
- Systemic osteoporosis.
Depending on the cause, osteoporosis is divided into the following cases:
Primary (related to the natural aging processes in the body):
- Postmenopausal (type I);
- Senil (type II);
- Idiopathic (in middle-aged and juveniles).
Secondary (due to illness or external causes):
- Rheumatic diseases, pathology of connective tissue (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Bexterev's disease);
- In endocrine pathologies;
- With blood diseases;
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- With renal pathology;
- With other diseases and conditions.
According to morphological criteria:
- Trabecular (loss of bone marrow);
- Cortical (loss of cortical substance);
- Mixed.
Symptoms of osteoporosis: how does the disease manifest itself?
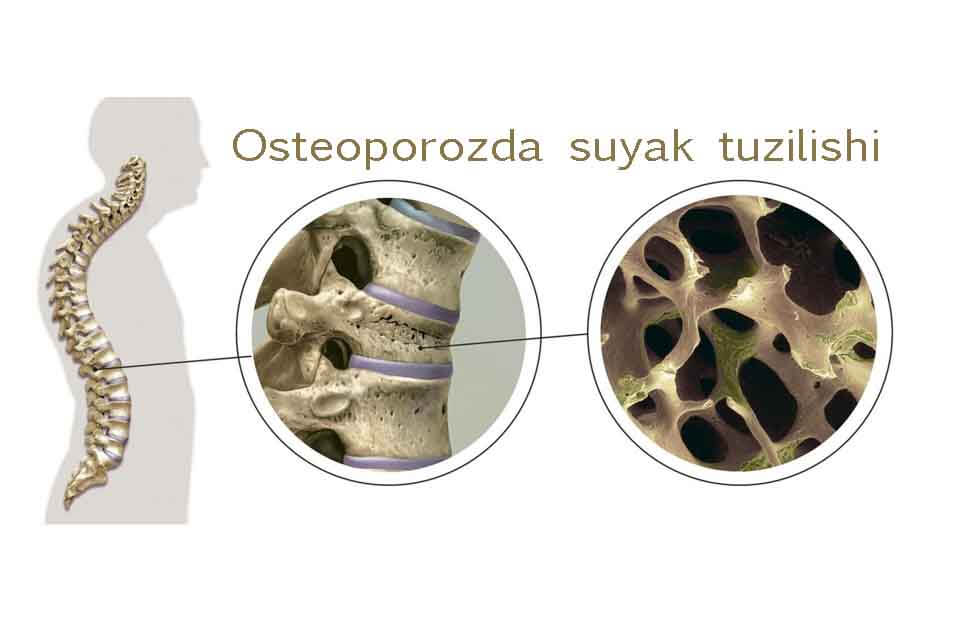
The disease can be latent for a long time. Often the disease affects the vertebral bodies. In a single vertebral fracture, the disease is often asymptomatic, and the pain syndrome results from fractures of several vertebral bodies. The most typical symptoms of osteoporotic spinal injuries are pain syndrome and spinal deformity (curvature). The pain appears acute and spreads along the intervertebral space to the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. Attacks usually occur as a result of a sudden twisting of the body, coughing, jumping, hitting an ax, or lifting weights. The pains in the morning are dull, increase during the day, and decrease slightly when you go to bed.
 Symptoms of osteoporosis, which may indirectly indicate the disease:
Symptoms of osteoporosis, which may indirectly indicate the disease:
- Fatigue (this indicates a general weakening or worsening of metabolism);
- Frequent cramps in the jaws;
- Occurrence of excessive care in the teeth;
- Severe brittleness of nails and their tendency to overlap;
- Pain in the bones and buttocks area;
- Premature graying of hair (this symptom is rarely observed);
- Intervertebral disc herniation (develops due to fragility of bone structures);
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Pre-diabetic status and early symptoms of diabetes are one of the direct symptoms of osteoporosis;
- Feeling of heaviness in the area between the shoulders;
- Decreased height;
- Curvature of the spine;
- Muscle weakness.
Other symptoms of the disease can include weight loss, changes in posture, and frequent bone fractures (usually of the spine, hip, wrist bones) even without traumatic effects.
Patient movement in osteoporosis
To prevent the development of the disease, the following is recommended:
- Running, walking, dancing and more.
- Follow your doctor's advice and be under constant supervision.
- Adherence to a healthy diet rich in calcium, vitamin D. Consume more calcium in soluble form (dairy products); refrain or limit the consumption of coffee, salty foods, smoking, alcohol; magnesium, potassium, phosphorus play an important role in the absorption of calcium, and the ration for these elements should be balanced; products rich in silicon, zinc, barium, copper, manganese, vitamin C, vitamins E, D, K should be preferred.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
Methods of diagnosis:
- Clinical examination and collection of medical history;
- Radiodiagnosis (radiography, tomography, densitometric methods);
- Biochemical research;
- Study of biopsy.
Treatment of osteoporosis
Treatment of osteoporosis is aimed at increasing bone strength. In mild forms of the disease it is enough to take calcium supplements with vitamin D.
In women with severe or progressive osteoporosis during menopause, estrogens are prescribed to slow the progression of the disease. Estrogens are often prescribed in combination with progesterone for treatment or prevention.
Bisphosphonates (zoledron, ibandron, alendron, clodronic acid) are also effective in the treatment of osteoporosis. They reduce the thinness of bone tissue, increase bone mass, and reduce the likelihood of fracture. Many experts recommend taking calcitonin for people with a broken spine.
Fluoride compounds help increase bone density, but the bones formed in this case become brittle. When men suffering from osteoporosis have low levels of testosterone in their blood, testosterone drugs are prescribed.
Direct bone fractures caused by osteoporosis also need to be corrected. When the femur is broken, a prosthesis is often required for a part of the bone. If the spine is broken, immobilization is performed, painkillers and physiotherapy are applied, but often the pain lasts a long time. When the wrist bones are broken, the bone position is replaced and plastered.
Complications of osteoporosis and disease prevention
The main complications of osteoporosis are fractures of the spine and peripheral bones, leading to discomfort, temporary disability, and increased mortality.
Maintaining physical activity, abstaining from alcohol and smoking, getting enough sleep, maintaining a normal amount of calcium in the diet (average 1200-1500 mg per day) and vitamin D can help prevent the disease. Also, the sun’s rays should be sufficiently exposed.
Notification: fresh dumps pin 2022
Notification: Derry escorts
Notification: dmt vape pen patent
Notification: Sbobet
Notification: sbo
Notification: reviews good cvv shop
Notification: limanbet login
Notification: Sbobet
Notification: max bet
Notification: youtube mp4 converter - y2mate
Notification: see website
Notification: land loan
Notification: Click here
Notification: official source
Notification: website
Notification: dragongaming
Notification: https://www.advantageja.eu/supplements/phenq-reviews-know-ingredients-pros/
Notification: thank you
Notification: news ball