SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Skill in using case technology and project method
Grid:
-
Development of case technologies. Ideas of the case-study method.
-
Case study method. Case processing technology.
-
Case study method. Concept of pedagogical design.
-
Pedagogical design objects. Pedagogical situation and its design.
-
Organizers and methods of their effective use.
1. Development of case technologies. Ideas of Sase-study method.
In the national personnel training program of the Republic of Uzbekistan, in the third stage of its implementation, special attention is paid to the training of competent specialists in all aspects. Development of the ability of independent creative thinking of personnel in market economic conditions is one of the main quality indicators of education. As the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan IAKarimov noted: "If children do not learn to think, the effectiveness of education will inevitably be low. Of course, knowledge is also necessary. But knowledge goes its own way, and independent thinking is also a great asset." Training students to become owners of this wealth is the main task of the educational system. Because, in the conditions of the market economy, only a person who has the ability to think independently and creatively will be useful both to himself and to the society - he will have the ability to solve his own problems.
The use of cases, which is widely used effectively in world pedagogy, firstly, develops students' ability to think, and secondly, connects the educational process with direct development (in our example, the educational process in vocational colleges). As Herbert Spencer said: "The great purpose of education is not to impart knowledge, but to teach action." Or, in the current educational system, in most cases, the goal of teaching is to provide knowledge to students as the final result, but at the world level, it should be recognized that the practical application of acquired knowledge is considered the final result of education. It is proof of our opinion that graduate students studying financial management at Harvard University (USA) have the right to receive a diploma only after solving 2,5 cases that can happen in banks during their studies.
The use of cases in the educational process forms the following necessary qualities in students:
-
develops critical thinking skills;
-
teaches to be truthful (objective);
-
forms an integral connection between theory and practice;
-
helps to formulate a new problem situation;
-
when solving situations, it allows to take into account the presence of factors affecting it and their impact;
-
forms the ability to accept the opinion of others;
-
teaches the culture of asking questions;
-
fosters a sense of responsibility for the decision made.
The following methods can be used when using cases: individual presentation, microgroup presentation, discussion in microgroups and then in a general group, role-playing games. When solving cases, it is necessary to pay attention to the following:
-
identifying the main problem;
-
identify the factors affecting the main problem;
-
separation of primary and secondary factors;
-
also consider an alternative solution to the problem;
-
making the most acceptable (optimal) decision.
When solving cases, analyzing it in a written way helps to understand the problem described in it more deeply, written speech is also one of the most effective ways to develop the ability to think independently and creatively.
In methodological development, some cases that may occur in the pedagogical process of vocational colleges and reflect a specific problem are recommended. In the compilation of these cases, some opinions of the trainees of the institute's training faculty and students of the special part-time department (pedagogical staff of the vocational college) were also taken into account. They can be used for the purpose of developing students' independent thinking and decision-making skills in the practical training of pedagogical skills.
Cideas of the ase-study method.
The idea behind the case study method is very simple:
-
The method is designed to acquire knowledge in subjects where the truth is pluralistic, i.e. there is no unambiguous answer to the question, but several answers, which are related to each other according to the level of truth. compete; the learning task in this case deviates from the traditional scheme and consists in obtaining not one but several correct answers and targeting them to the problem area.
-
The emphasis of teaching is not on the acquisition of ready knowledge, but on the cooperation of the student and the teacher on its development; The principle difference of the case-study method from traditional methods is that there is democracy in the process of acquiring knowledge, where the student has equal rights in the process of discussing the problem with other students and the teacher.
-
As a result of using the method, not only knowledge, but also professional skills are obtained.
-
The undoubted advantage of the situation analysis method is not only the acquisition of knowledge and the formation of practical skills, but also the development of students' values, professional positions, life guidelines, a sense of their own professional life, and the development of a life changing system. .
-
The case-study method overcomes the shortcoming of the "dry" emotionless presentation of the material - in this method there are so many emotions, creative competition and struggle that the discussion of a well-organized case resembles a theatrical performance.
-
Case study method. Case processing technology.
"The homeland of the Case Study method is the United States of America, more precisely, the Business School of Harvard University." It was first used in 1924. The principle of "precedent" or "event" was the basis for the arrival and development of the case method. This method is widely used in economics and business sciences abroad.
The method of specific situations (case-study method) belongs to non-game simulation active teaching methods.
The purpose of the case study method is to analyze the case situation and develop a practical solution with the joint efforts of the group of students. The end of the process is to evaluate the proposed algorithms and choose the best one in the context of the given problem.
Case content
The use of cases in the educational process forms the following necessary qualities in students:
-
forms an integral connection between theory and practice
-
develops the ability of critical thinking
-
teaches the culture of questioning
-
when solving situations, it allows to take into account the presence of factors affecting it and their impact
-
fosters a sense of responsibility for the decision made
-
forms the ability to accept the opinion of others
-
teaches to be truthful (objective).
-
helps to formulate a new problem situation.
Case processing technology.
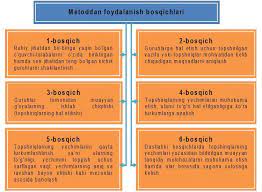
The technology of working with cases in the educational process:
-
Individual independent work of students with case materials (identification of the problem; description of important alternatives, proposals or recommended actions).
-
Working in small groups to match a critical problem and its solution.
-
Presentation and examination of the results of small groups in a general discussion (within the study group).
A good case should meet the following requirements:
-
Conformance to the clearly stated creation purpose.
-
Having a corresponding level of complexity.
-
To be relevant at the time of working with him.
-
It should not wear out too quickly.
-
Development of analytical thinking.
-
Describe typical situations.
-
Causing controversy.
-
Having several decisions.
-
Concept of pedagogical design.
Every day, the engineer pedagogue sets before himself the goals of educating, teaching or educating young people. Also, following the principles of education, the student forms the content of his activity, the activity of students, chooses the methods and means of its implementation, and strives to improve the forms of giving it to students. This is the most general and simplified algorithm of pedagogical activity aimed at creating a pedagogical process.
This is the first step towards the creation of a complex technology of education. The next, relatively responsible step is to bring other components into a single, whole and mutually proportional system. For this, the teacher should acquire the theory of pedagogical design.
Pedagogical design is the preliminary thinking and logical development of the main parts of the future activities of students and pedagogues. The term design entered pedagogy from technical knowledge. Designing in engineering means an advanced estimation of the work to be done later on in reality. The increase in pedagogical knowledge, the increase in methods, tools and forms of education, the expansion of factors affecting educational relations have led to the fact that pedagogical activity has become an increasingly complex profession. It is becoming more and more difficult for the teacher to acquire this knowledge, especially to use it. That is why the science of pedagogy is forced to avoid developing only technocratic recommendations.
Algorithm of educational technology design
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
Technocrat means profession, craft, "management art", entrepreneurship.
Proponents of this direction in pedagogy are sure that effective pedagogical techniques will replace the amorphism in the issues of youth behavior management, i.e., lack of form.
For an engineer and pedagogue, terms such as "design", "technique", "technology" are relatively familiar and understandable. It is as if these concepts connect the two functions of his activity, allow him to discover the commonality between them and make his work much easier.
Pedagogical design, which includes the most productive ideas of technical design, is the ability to get out of a situation that seems to us chaotic, to enrich pedagogical knowledge. Pedagogical design allows to optimize the activities of the master of industrial education and teachers of technical subjects.
Pedagogical design is a function of any pedagogue, whose organizational, gnostic (that is, the ability to communicate with a student, establish communication, find ways to relate, creativity, inventiveness) or communicative abilities are superior. can be. According to pedagogical research, technical science teachers spend 28% of their working time on this function, and industrial education masters spend more than 11%.
Due to the ability to design educational processes in schools and vocational colleges, it ensures that this complex process remains technological.
-
Pedagogical design objects. Pedagogical situation and its design.
The essence of pedagogical design is to be able to foresee it, to see its results in order to create approximate options for the future activity. In this case, the main attention of the pedagogue should be focused on the innovation mechanism created and on the continuation and application of this or that action, process and system.
In fact, what exactly does an engineer-pedagogue design? It starts with defining design objects. We have already mentioned one of these objects - it is a pedagogical process.
This, in turn, is divided into pedagogical situations arising from it. These are its components. They are characterized by the transition from one state of the process to another. The pedagogical process itself is part of a more complex device, that is, the pedagogical system. "Minor" situations are part of the process, and the process is part of the system. ("Matryoshka dolls").
For example, we work in the education system or we work in the vocational training system. In both cases, the term "system" has common features. We will try to open them.
Let's say that in order to help students to choose a profession, it is necessary to conduct career guidance among school students.
The pedagogue begins to mentally collect all the factors that affect the choice of profession (family, audience, media information, street-neighborhood, psychological possibilities of the teenager, especially the needs and possibilities of production enterprises). All these factors are very important in the career guidance system.
Pedtyzym comes in small, medium, large and super large. The sub-system includes some systems of educating students. For example, the system of industrial education in colleges consists of extracurricular activities of students, guidance system for choosing a profession, legal education, trade union work, environmental education and others. A medium-sized system consists mainly of pedagogical activities of colleges, and a large system consists of district, city, and regional educational systems. It usually consists of a large socio-pedagogical complex, which, in addition to schools and educational institutions, also includes cultural institutions, production enterprises, household and domestic service institutions, as well as management departments of the area.
Designing a sub-system is a complex process, consisting of parts with different quality indicators. For example, the system includes people - pedagogues, students, material equipment - educational equipment, electronic computers, the functions they perform.
The supersystem (extremely large system) includes large areas in terms of size and purpose, systems created on the scale of the republic.
This system consists of our students and ourselves. Each system has its own set of parts and its own purpose. For example, the vocational education supersystem includes the content of activities related to the training of future workers, its structure, principles, pedagogical processes, students, pedagogues, parents who are participants in the process, production events, their rights and duties. , includes management of the pedagogical system, material and technical support, educational-methodical, scientific, financial-economic and legal-legal support complex.
Knowing the components of the design system is very necessary for any pedagogical system, although their complete set is not always provided, it is important for the work of the pedagogue. The introduction of EHM into the field of education has helped to improve self-improvement and work on oneself.
Pedagogical systems are a unique product (product of the process). Each of them has its own unique characteristics:
-
they always have their own goals: to develop students and teachers, to protect them from the negative effects of the environment;
-
each of them is organized as a system and can change its functioning under external influence, and even if it receives this influence, it is able to soften it, turn it in the necessary direction, level it, strengthen it.
What specific pedagogical systems does the engineer pedagogue work with? With practically all types of systems. In fact, the republican, regional, regional, city, district educational system defines and directs the activities of relatively narrow systems - schools, colleges, and higher educational institutions. They, in turn, affect the system of professional preparation of students, their aesthetic education, and their activities. Pedagogical processes are created within the systems. In turn, the pedagogical system forms the creation of favorable conditions for the creation of pedagogical processes. Thus, the pedagogical process is the most important design object for the pedagogue.
Pedagogical process is the integration of all components (factors) that ensure student and teacher development and direct interaction.
In the educational supersystem of the country or region, conventions, conferences, Olympiads, competitions, "round tables", "pedagogical studies" are held, newspapers and special forms of press are organized, etc. Small and medium pedagogical systems are designed for larger pedagogical processes.
Pedagogical situation and its mudhchoose.
It always exists within this or that pedagogical process, through which a pedagogical process is created within a certain pedagogical system.
Pedagogical situation is a component of the pedagogical process, which determines its situation at a certain time and place.
Pedagogical situation is always concrete, it is created or arises during a lesson, during an exam, during an excursion, etc., usually it can be solved immediately. The design of the pedagogical situation is part of the design of the process itself.
The ability to create and solve a pedagogical situation is very important in pedagogical activity. Because the pedagogical process is manifested only through them. These small parts embody all the achievements and shortcomings of the pedagogical process and the pedagogical system as a whole. The concrete expression of educational relations realizes the possibilities of pedagogical situations.
The structure of the pedagogical situation is very simple in appearance. It includes two subjects of activity - teacher and student, and methods of their interaction. But this simplicity can be deceptive and disappointing (flattering, begging or bluntness may not always give the same result in the activity). The interaction of the participants of the pedagogical situation depends on their complex inner world, the level and level of their education, and may even cover all its components in one way. For example, a master of industrial education wants to alleviate the tension of one group of students against another, individual student. It projects the situation by assuming that the student is a wonderful person, beautiful and honest. For this, he advises to give assignments, organize parent appearances in front of children, and use such things as confidence and encouragement.
Pedagogical situations can arise by chance or by design. But in both cases, solving it requires thinking.
The design of pedagogical situations is carried out as a process of "adaptation" of the pedagogical process, taking into account concrete people to the smallest detail of the real situation. In pedagogy, the relationship between the teacher and the students is considered to be unchanging. In fact, the addition of a third person to the conversation between the teacher and the student or the intervention of an event unrelated to the topic completely changes the situation.
Each pedagogue participates in the design of three types of objects: pedagogical system, pedagogical process and pedagogical situations. All of these are interconnected, designed with their integrity and interconnectedness in mind. We can see this in the diagram below:
The structure of the pedagogical system depends on the quality of the pedagogical processes, the quality of the pedagogical process, the pedagogical situation, and especially the pedagogical situation depends on the quality of educational relations. So, during the pedagogical process, it is necessary to look for an unpleasant situation first from the pedagogical situation, then from the process itself, and finally from the pedagogical system. Or it can be determined that the general condition is in its design.
-
Organizers and methods of their effective use.
Basic information
In addition to traditional paper and electronic organizers, there are unusual options, for example, some issues drawn in terms of content are fixed on Whatman paper with the help of stickers, which is then glued to the wall.
With the development of information technology, the book began to be replaced by personal pocket computers, computer programs and online organizers with additional functions: reminders about upcoming events, information protection and synchronization.
In the 21st century, the term organizer began to be understood more and more by software for mobile devices. Their undoubted advantage was the practically unlimited amount of data entered, as well as the setting of automatic reminders. The shape of organizers can be different. For example, narrowly specialized organizers: recipe organizer, finance organizer, music collection organizer.
An organizer can also be a time management tool. Planning ahead can increase the efficiency of any personal or professional activity. Therefore, a person who advises organizations and private individuals in the field of improving the efficiency of time management is sometimes called an "organizer". There is even a National Association of Professional Organizers (NAPO) in the US.
Pocket personal computers.
The development of pocket personal computers (PPCs) began with electronic organizers. These were calculator-sized devices with address information storage, event scheduling, diary keeping, and built-in software, etc. Today, ChKK is a complex device with a multitasking operating system. To turn it into an organizer, you need to install the corresponding software.
Computer program-organizer.
A computer program-organizer is a computer program related to application software designed to collect user information, then quickly search for information from it, organize tasks and monitor their execution, and monitor certain events. . It is one of the forms of private organizer.
The functions of a typical computer program-organizer are related to ensuring the operation of the following departments:
-
calendar;
-
contact manager (user's address - phone book);
-
notebooks and papers (analogue of sticky-sheet papers);
-
events tied to a specific date and time (eg, holidays or meetings);
-
scheduler of tasks (assignments) — control of their independent or external execution;
-
alarm clocks that remind the user about certain events.
Some program-organizers may not have any of the sections listed above, or may perform an additional functional task, for example, perform the function of a mail client, allowing you to work with e-mail.
The online organizer differs from a regular program in that it is installed on the workstation instead of on a local computer.
Planing Organizers Black Organizer Large Gray Organizer
Time management using a computer.
The time when www.improvement.ru.site was found is the starting point of the systematic application of time management.
It is necessary to develop a special program for storing, structuring and describing issues, projects and ideas, studying different methods of time management.
Paper organizer
The paper organizer includes:
1. Operational management
It is usually a 48-page notebook, two pages of which hold exactly two weeks. 7 days of the week are drawn on the sheet on the right, notes are written on the paper on the left. The notebook is always at hand, on the work table, for quick recording of issues. In this notebook, only the issues of the days are written briefly about what to do, without explaining in detail. The notebook does not fully explain what the projects are and when they should be completed. This is where information is written from the thick "Strategic Planning" and "Project Cards" in the weekly planning of issues.
When you need to do a lot of work (for example, on the street, in the store, in transport, etc.), then write down the issues from the "Operational Report" notebook on a separate piece of paper, and walk with this piece of paper throughout the day and review the completed work. must be turned off.
"Operational report" notebook
-
Strategic planning.
It is a 96-page notebook where you can write plans for months/years. It can be as follows:
-
Monthly goals. 12 months, where 1 sheet q 1 month.
-
Annual goals.
"Strategic report" notebook
"Development" group projects (blue folders)
Project folders
3. Electronic organizer.
After developing LeaderTask - the organizer, all the shortcomings of the paper organizer were simply solved. Now, instead of spending a lot of time filling out papers, you only need one notebook, which is a computer, in which you can enter and process as much information as you want, and process it in a way that is convenient and acceptable for you. You can save it and print it.
Electronic organizer Organizer Atlantic Business people
Planning organizers for 3Com PalmPilot
QReferences:
-
Azizkho'jaeva NN Pedagogical technology and pedagogical skill.-T.: TDPU. 2006
-
Sayidahmedov N. New pedagogical technologies. -T.: "Finance" publishing house, 2003. - 171 p.
-
Ochilov M. New pedagogical technologies. - Against. "Nasaf", 2000-80 p.
-
Tolipov U., Usmanbayeva M. Pedagogical technology: theory and practice.-T.: "Fan". 2005.
-
BL Advanced pedagogical technologies. - T.: 2001
-
Klarin MV Pedagogical technology and teaching process.-M.: Znanie.
-
Pityukov V.Yu. The basis of pedagogical technology. — M.: Gnom-Press, 2007 (uchebnoe posobie).
-
Ishmatov Q. Pedagogical technology. Lecture text. Namangan, NamMPI.-2004.-95 p.
-
Alimov NN, Turmatov JR "Pedagogical technologies". - Jizzakh, - 87 pages.
-
Dadamirzaev G'. Basic words and phrases for pedagogical technologies. Methodical guide. — Namangan, NamMPI, 2008, 30 pages.
-
Seytkhalilov A., Rakhimov BX, Majidov IUPedagogicheskiy slovar-spravochnik. - T.: "OPTIMAL LIGHT", 2011.-704p., 2011.-704p.
-
zyyonet.uz
-
tdpu.uz