SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Egg cells are a new life-giving miracle. In the ovaries, the egg cells are surrounded by a shell. This shell is called the follicle. As the egg cell matures, so does the follicle. The follicular cavity is filled with fluid, in which the egg cells are also located.
Contents [Close]
- How does follicle growth and maturation take place?
- Follicle maturation
- Phases of the menstrual cycle
- Monitoring of follicle maturation in UTT
- Follicular developmental delay
- What causes a follicle not to rupture?
- Absence of follicles
- What causes follicle immaturity?
- Improper development
How does follicle growth and maturation take place?
Follicle maturation
The ovarian follicles are the islets that surround the egg cells. Immature young follicles pass into the ovary during embryogenesis. The total number of immature follicles migrated at birth is about 1-2 million. Most of them are then absorbed, and by the time a girl reaches puberty, she will be close to 300.
During puberty, about 10 follicles mature during each menstrual period under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormones. As the mature egg approaches the exit of the cells (close to the ovulation period), a dominant follicle is formed. Its volume continues to increase, at which point a small cavity is formed in the ovary, which is filled with fluid.
Near the time of ovulation, this cavity reaches a diameter of 2 cm and is called a graafian bubble. The diameter of the secondary follicles is smaller. The egg cells "float" in the fluid in the graphene bubble.
During the maturation of the follicle that surrounds the egg cells, the female sex hormone - estrogen - begins to be produced. It takes an average of 2 weeks for the follicles to mature. One day before the ovulation period, the amount of estrogen hormone suddenly rises, which leads to the release of luteinizing hormones. The dominant follicle ruptures during ovulation, from which egg cells ready to be fertilized emerge. The remaining follicle is absorbed.
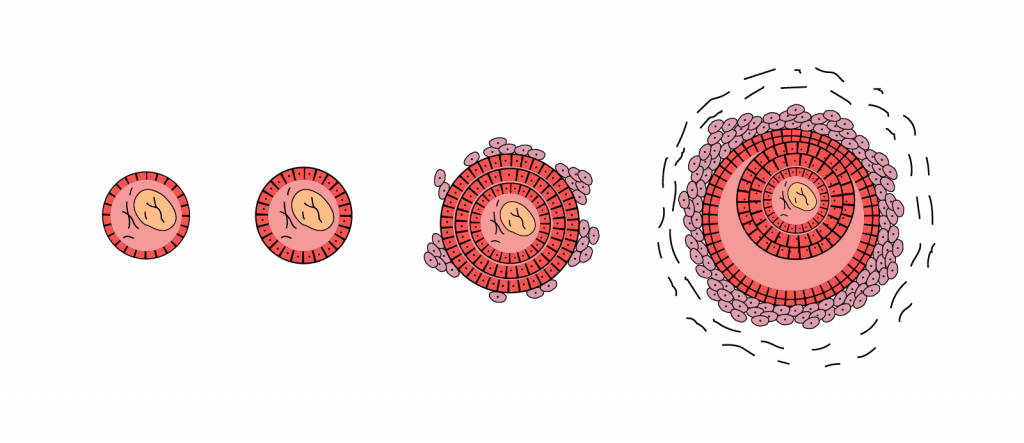
Follicle development
Phases of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is divided into phases depending on the location of the follicles and their size. The phase that begins after menstruation is called the follicular phase. The period during which an egg cell follicle ruptures is called the ovulation phase.
The luteinizing phase begins at the time of ovulation. Graaf vesicle cells form a yellow body after the egg cells hatch. The corpus luteum begins to produce the hormone progesterone. The function of progesterone is to prepare the uterine endometrial lining for fertilized egg cell implantation. If there is no fertilization, the corpus luteum is absorbed before menstruation.
The changes in the ovary continue to look like this. Now let’s answer the question most women ask: how big should the follicles be?
Also read this article: Infaltil is an underdeveloped uterus
During the examination, the follicles are clearly visible on the UTT (UZI) screen. In order to know the changes taking place in the follicles and ovaries, it is advisable to conduct frequent UTT in them. Examination reveals an average of 1-2 to 4-5 follicles. Normally, in some cases, 2-3 dominant follicles may also appear.
In some cases, for example in ECO (extracorporeal fertilization), 4-6 dominant follicles are formed by stimulating the follicles. Special syringes containing chorionic gonadotropin (XG) are used to stimulate the follicles. If you believe in only 1 follicle and perform ECO, the percentage of results will be low.
Monitoring of follicle maturation in UTT
The menstrual cycle, which is characterized by the very large size and abundance of follicles, is indicative of pathology. Against the background of hormonal changes can occur a variety of diseases. For example, follicular and luteinizing ovarian cysts. This results in the formation of mature, large follicles without the ovulation process. Impaired follicular maturation and lack of ovulation is one of the symptoms of infertility in women.
UTT monitoring is performed to rule out that infertility is caused by impaired follicular maturation. To do this, the ovaries are examined at UTT for several days. The size and number of follicles are determined. The test is called folliculometry.
On the seventh day of folliculometry, the follicles are detected in a small, 5-6 mm in diameter, fluid-filled ovarian cavity.
On day 11, the size of the follicles is determined by a diameter of 10–12 mm. The dominant follicle can be identified with extreme precision.
On the 12th day, the follicles occupy a volume of 18 mm in diameter. The detection of a large follicle, i.e. 21 mm, indicates that ovulation is imminent. Usually this happens in the middle of the menstrual cycle, days 13-15. An oversized follicle 28-30 mm or larger indicates the formation of a follicular cyst. Such cysts are often considered functional and disappear spontaneously.
On the 14th day, ovulation is observed. After the dominant follicle ruptures, it disappears or shrinks in size.
After ovulation, as mentioned above, the follicles turn into a yellow body. The amount of the yellow body hormone - progesterone - plays a big role in getting pregnant. If the amount of this hormone is less than necessary, the pregnancy will not be observed or will end in the early stages. In such cases, the yellow body is said to be deficient. To rule out this pathology, a UTT test is continued and the amount of progesterone in the blood is checked.
Follicular developmental delay
As mentioned above, in follicle maturation, they go through certain stages and then mature. In the early stages, the follicles mature in the same way, all the follicles begin to mature at the same time. Over time, one of them accelerates in growth and becomes dominant. The size of the dominant follicle reaches 15 mm, and the rest undergo atresia (regresses, is absorbed).
Also read this article: EKU - artificial insemination
Rupture of the dominant follicle is an important process because mature egg cells emerge in this way.
What causes a follicle not to rupture?
In women, the question often arises, why do mature follicles not rupture? There are many reasons. The answer is a thickening of the wall of the follicle or a hormonal imbalance. If the corpus luteum is formed early, that is, before the follicle ruptures, it is called a non-ovulated follicle. In this case, the dominant follicle may also mature normally. Later, even if this follicle does not rupture, a yellow body will still form. This means that even when mature, egg cells cannot emerge from an unbroken follicle due to the thickness of the shell, and fertilization and pregnancy are not observed.
The next reason is persistence. In persistence, a dominant follicle is formed, the follicle matures normally, but does not rupture. The persistent follicle is maintained throughout the menstrual cycle. It should also be noted that the persistent follicle can be preserved after the menstrual cycle. Specific features of this condition are: absence of corpus luteum, increase in the amount of estrogen hormone, decrease in the amount of progesterone, lack of free fluid in the uterine cavity.
Absence of follicles
If a woman is found to have no follicles, it indicates ovarian dysfunction. In early menopause, ie before the age of 45, the absence of follicles is detected. From a medical point of view, this is not normal. And in order to treat this condition, hormonal therapy is recommended, trying to restore sex life.
The difficulty of ovulation in women is also reflected in the background of the prolongation of the menstrual cycle. If the menstrual cycle begins longer than 35 days, or earlier than 21 days, it is an indication that there is a risk of proliferation of immature or viable egg cells.
What causes follicle immaturity?
Responses to this include early menopause, ovarian dysfunction, ovulation problems, follicle immaturity, or the formation of empty follicles. This is a problem for young women, and requires treatment. However, this may be the norm for older women.
Occasionally, menstruation without ovulation is also observed in women. This period is called the "rest" period or ovarian regeneration. This condition is also observed in some healthy women 2-3 times a year. After the age of 1-33, this condition can increase up to 34-3 times a year.
The incidence of anovulatory cycles increases with age. In addition, thin, strict diet women often complain of lack of ovulation and lack of menstruation. The amount of estrogen produced is also reduced, so the menstrual cycle is also lost.
Also read this article: Seven tips for those who want to lose weight
Improper development
UTT diagnostics is used to detect infertility caused by malformation. The test is usually done 8-10 days after the start of the cycle and after menstruation. After the examination, the doctor may say:
-
Normal ovulation;
-
Dominant follicle regression (shrinkage);
-
Persistence;
-
Follicular cyst;
-
Luteinizing;
-
Follicle failure.
Notification: DevOps Services
Notification: verybigblog
Notification: สล็อต pg เว็บ ตรง
Notification: sbo
Notification: sportsbet io login
Notification: Pico Finance
Notification: buy magic mushrooms online usa
Notification: leaf
Notification: this website
Notification: psychedelic mushroom chocolate bars legal in tennessee
Notification: remington firearms
Notification: https://www.dallasnews.com/marketplace/2023/09/29/phenq-reviews-legit-diet-pills-or-fat-burner-scam/
Notification: https://www.buoyhealth.com/blog/health/phenq-reviews
Notification: notebook bandar togel