SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Ethernet, FDDI local network technologies
Plan:
Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
-
Emergence of local network…………………………………………………….
-
BlueTooth is a wireless network………….........................................................
-
Working with the internal ports of the computer................................................ ..
Conclusion………………………………………………………………………………………………..
List of used literature……………………………………………………..
Introduction
The purpose of information technologies is to produce information for human analysis and to make a decision on performing a certain behavior based on it. Information technology is a process that uses a set of tools and methods of data collection, processing and transmission to obtain new quality information about the state of an object, process or event (information product).
In addition, the main goal of information technology is to organize information storage and transmission.
The information system represents the information-computer system of information processing. Information system - reflecting the process of joint activity of computers, computer networks, information and software and people, it undertakes the production of information for the consumer.
The main task of information systems is to create opportunities to manage the flow of events and processes. Also, based on information, the goal is predetermined, and the program to achieve this goal has a purposeful effect on the produced controlled process.
The main tasks of information systems in education are the development of information needed by the consumer with the help of the most optimal management methods of all information resources related to the studied object, and informational and technical for their use in the management of the educational object. is to create a supply environment.
The importance of transmitting information from generation to generation is consistent with the importance of education.
Information technology (IT) is the process of collecting, reassembling, restoring, storing, expressing, systematizing, transmitting and making it convenient for the consumer with the help of computers and telecommunication tools in order to find solutions to system problems. is a set of organized practical programs.
Information technology is the main source of process management. It includes sorting and processing the prepared data into the system and transferring the processed data for the required purposes.
Informatization is not only a scientific and technical achievement, but it can always be an important factor in the development of education, training, art, medicine, economy, agriculture, industry and similar fields.
On the basis of modern computer technology and means of communication, modern methods of collecting, storing and transferring information to the necessary sources continue to develop, that is, computerized methods.
The emergence of information technology has revitalized the work in this field, that is, now life requires the creation of not only information, information technology, but also information systems, and from them, service systems such as knowledge bases, tasks, logical conclusion solving machines. is demanding. Solving these demands depends on social reforms.
The role of innovative technologies in organizing the educational process of higher education is increasing day by day. The use of distance technologies has further expanded the possibilities of modern education. Today, it is possible to get an education from anywhere in the world, using the opportunity of modern information and communication technologies (ICT). Although traditional education maintains its position, distance learning technologies are becoming popular day by day.
Today, in our country, an educational system aimed at integration into the new world information-educational environment is being established. This is followed by significant changes in the organization of the educational process that respond to modern technical capabilities. The introduction of modern information technologies into the field of education makes it possible to qualitatively facilitate and change the methods of education and the forms of organization of the teaching process based on a new approach. Information and communication technologies are the most important part of the process of modernization of the educational system. ICT is information processing methods with various technical and software devices. It is primarily computers with the necessary software and telecommunications equipment on which data is stored.
Article 1997 of the Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan "On Education" adopted on August 29, 1 defined the legal basis of education, upbringing, and vocational training of citizens and the constitutional right of everyone to receive education. it was emphasized that it is aimed at ensuring the right. The current period shows a high need for new requirements of the educational stage. The use of distance learning technologies in the educational process and its management also play an important role in this. In this regard, a number of urgent works are being carried out in our Republic.
Since 2012, a unified videoconferencing educational technology has been implemented among all higher educational institutions (HEIs) of the Republic of Uzbekistan, and now a lot of attention is paid to electronic education in this regard. Planned work is being carried out to open up new opportunities and prospects for HEIs. For example, remote management of personnel qualifications in regions is an example of this. The new stage of electronic or distance education envisages not only the use of information technologies, but also the provision of educational resources in electronic form.
At Uzbekenergo JSC, large-scale work is being carried out to raise the quality of the introduction of information and communication technologies to a new level. In particular, in accordance with the decision of the Head of our State on October 2018, 23, on November 30 of last year in Tashkent, with the South Korean company KT Corporation, the introduction of information and communication technologies to a new level in terms of quality in the automated electricity accounting and control JSC "Uzbekenergo" large-scale work is being done to raise it. In particular, in accordance with the decision of the Head of our State on October 2018, 23, on November 30 of last year in Tashkent, South Korea's company "KT Corporation" signed an automated system of accounting and control of electricity, SCADA - automated dispatching system, and information management systems (ERP). an agreement was signed on the establishment of a single republic data processing center. In this Center, it is planned to use the most modern equipment of leading manufacturers. Currently, work on the implementation of the automated system of accounting and control of electricity, which covers all enterprises of the energy system for the production, transportation and distribution of electricity, including all consumers of electricity, as well as the SCADA - automated dispatching system started The 1st stage of the automated system of electricity accounting and control project (in Bukhara, Jizzakh and Samarkand regions) will be organized at the expense of the saved funds of the Asian Development Bank and will be launched by September 2019, 1. In addition, in order to solve the issues of financing the creation of the SCADA - automated dispatching control system, on January 11 of this year, at the head office of "Eximbank" in Seoul, the deputy chairman of the board of "Uzbekenergo" JSC Jahangir Obidjonov and the director of "Eximbank" Won Suk Ha o a meeting was held between At the end of the meeting, an agreement was reached on the allocation of a grant for conducting appropriate research and preparation of the technical and economic basis of the project with the help of highly qualified foreign consultants. After the technical and economic basis of this project is approved, "Eximbank" will allocate a preferential loan for the project for a period of 20 years. Notably, introduction of SCADA - automated dispatching management system helps to increase the reliability of electricity supply to consumers by optimizing the operating mode of electrical devices and preventing emergency shutdowns caused by human factors.
1.1 Emergence of local network
One of the reasons for the emergence of computer networks is the cooperative use of resources and the expansion of individual computer capabilities. Through the network, users can simultaneously work with the same information and copies of files, applications. This situation saves space on data carriers. In addition, the combined use of a printer, scanner, modem, laser disk set saves additional money.
When using the network, the reliability of information storage increases, because valuable information can be copied again in a very simple way, and the exchange of information between individual users is facilitated. The network embodies the request of users, allows many customers to use information at the same time.
A set of computers that can interact with each other through hardware devices and network software network is called.
Networks can be classified according to different standards. These are:
1) bandwidth, that is, according to the speed of data transfer to the network:
— down to 100 Kbit/s;
— medium 0,5-10 Mbit/s;
— higher than 10 Mbit/s.
2) the speed of working with long-distance communication networks, according to their physical measurement:
- LAN (Local-Area Network) local network (one office, intra-building communication);
— CAN (Campus-Area Network) — a campus network, a computer local network connected to each other by telephone or modems, but located far enough from each other;
- ME (Metropolitan-Area Network) an expanded network that transmits information to a large radius (several tens of km) with the possibility of high-speed communication transmission (100 Mbit/s);
— WAN (Wide-Area Network) a large network connecting separate networks provided with large-scale (regional) special devices and programs;
— GAN (Global-Agea Network) global (international, intercontinental) network;
3) by the type of network nodes (a node is a place where computing networks and their separate elements are connected). In other words, the node includes personal, mini- and large computers, as well as a separate network. For example, individual computers (otherwise called stations) on public networks are examples of nodes. Individual networks that are not so large will be nodes for the campus network.
4) according to the relation of nodes:
— computers of the same color (peer-to-peer), not too big, with the same position (here all computers are both "client", that is, an ordinary user of the network, and "server", that is, to network users may be a service provider). Macalan, WINDOWS 95 OS network distributed (Distributed) networks. In this case, servers serve network users, but do not manage the network;
- server (Server based) or networks with centralized management. Here, the main element of the network is the server. The remaining nodes can use the server's resources (for example, Novell NetWare, Microsoft LAN Manager, etc.).
5) on the use of network operating systems (network OS):
homogeneous - all nodes use the same or similar operating systems (for example, WINDOWS OS network);
heterogeneous — several network operating systems are used at the same time (for example, Novell NetWare and WINDOWS).
Networkq service
A network can have several different servers. It is very important what kind of services a computer network offers to its customers, what kind of service they provide. Let's get to know them:
-file — server — allows the client to use files stored on information storage devices. In this case, the server must allow access to files from all workstations. Also, the task of being able to protect information is solved positively;
— print — server generally provides service to many customers through multiple printers. In this case, the server must be able to receive the information to be printed and print them in turn;
—fax server- provides customers with integrated network service with fax-modem telephone networks. It's like outputting information (like a printer). Fax messages received by the fax server are processed on a separate network.
-e-mail (E-mail) — provides information exchange between clients, regardless of how far they are from each other. Here the process is just like regular mail. An e-mail has its own address. If we call it the sender, the receiver also has its own address. "Letter" is placed in the mailbox (that is, the mail server) and is delivered to the mailbox of the recipient by means of a system of mail servers, that is, special directories of the sender and recipient are placed on the computer serving the client. In this way, the messages are transmitted as files.
- direct communication (Chat), which means that two or more clients exchange information (text, sound, video) at a specific time with the help of special software. When using digital video cameras, sound cards, microphones, multimedia tools, it becomes possible to hold video conferences. In such cases, computers must be of high performance and network bandwidth must be strong. MS Net Meeting – It is possible to communicate directly through the program.
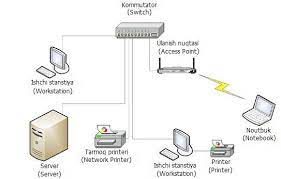
Local computer networks
Global networks, as you know, cover large cities, countries, continents. Local networks cover a fairly small area. They are intended to serve up to 10 customers within a radius of 100, 1000, 1000 meters. Such a size allows LKT to work at an acceleration of 10 Mbyte/s and more. Usually LKT consists of interconnecting workstations (IS) and special computers (file, print servers, etc.) with a cable. They, in turn, are connected using network adapters (network cards).
The methods of connecting individual nodes in a network are called network topology. Three topologies are commonly used:
-
General tire. In this case, all computers in the local network are connected in parallel to one communication line. Management of such tires can be both separate and centralized. In centralized management, a special computer-server is connected to the network, its task is to control the transmission of information in the network. In separate management, all computers have the same status, they have the ability to transfer data independently.
-
People. In this case, all computers are connected in series, like a closed loop. In this case, the message is transmitted one after the other from computer to computer. The process continues until the computer that sent the message receives the same message again.
-
An asterisk. Networks with star topology have a central node (switch or concentrator). All other computers are connected to this central node. The first transmitted message arrives at this device, and then it is transmitted to other computers.
Cables used for binding transmission medium is held as
Cables are mainly divided into three:
-coaxial cables (coaxial cable), they are very similar to the television antenna. Transfer speed: 10 Mbit/s. It is mainly used to create an indoor network.
-twisted pair cables resemble a telephone wire. Transfer speed: 100 Mbit/s. It is mainly used to create an indoor network
.
- fiber optic cable (feeder-optic cable). The most reliable and fast, but at the same time very expensive type of cable. It is used for a network with a distance of 100 km. Transfer speed: 2 Gbit/s.
Network cable technician kindicator
Cable type |
Transfer speed,Mbps |
The distance between the points forming the network |
Ability to recover when the cable is disconnected |
Cost |
Coaxial cables |
10 Mbit/sec |
500m |
Past |
100 soums/meter |
Twisted pair cables |
100 Mbit/sec |
100m |
good |
200 soums/meter |
Fiber optic cables |
1-2 Gbps |
100 km |
Special equipment is required |
1000-3600 soums/meter |
The field of application of local networks is very wide. This includes automation of office work, enterprise management systems, project automation technological processes and robotic complexes, banking and information systems, management of e-mail systems.
It must be recognized that it is very convenient to configure and use the local network in WINDOWS OS. Before working with the network, if your computer is not connected to a local network, configuration work will be carried out. The process of setting up a computer to work on a network is as follows:
First of all, you need to make sure that there is a network card (card) in the computer.
Wires are connected to the RJ-45 jack through a special connector. - connector.
The Boot Rom chip allows you to boot the operating system using another computer on the network. Wires are connected to HUBs to form a network.
Connecting a computer to a network using a HUB (Switch) device. Hubs are needed to connect computers in a room to each other, while switches are placed between buildings.
Any computer working on a network must have its own name, a specific TCP-IP address, and a workgroup. Other network participants can refer to it with the same name and TCP-IP address (file and folder, message sending). Ping to check for communication between computers with Windows OC installed (where the address of the computer being checked on the TCP-IP network) command is used. For example, ping 10.1.14.27.
BlueTooth is a wireless network.
BlueTooth is a wireless network standard. Operating radius is 10-100 meters and operates at 2.5 GHz frequency. The transfer speed is 1 Mbit/sec. Of course, devices must also be designed for this standard. It is also possible to communicate with a hand (mobile) phone. If the telephone operator (for example, Uzdunrobita) allows you to connect to the Internet, then it is possible to connect to the wireless Internet using a computer and a mobile phone (very convenient for laptops).
1.2 Principles of organization of computing networks
In information technologies, a port is a connection between the sending and receiving information (logical or physical). Usually, the following are:
Hardware ports - this is basically the physical device of the computer, which is mainly connected to the computer using a plug or cable. They include:
Parallel port, Serial port, USB, PATA/SATA, IEEE 1384 (FireWire), PS/2
Input-output port - enables data exchange using devices on microprocessors (for example, Intel). The input-output port is used to provide data to the program and exchange it.
The network port is a TCP and UDP protocol parameter that determines whether a data packet in IP format is used.
Computer peripheralsforms the process of information exchange with i, the external interface of the computer. The external interface consisted of a set of external ports, buses, computer interfaces and external devices. Buses are mainly used to connect computers and external devices.
Connecting a printer, scanner, mouse, keyboard, and similar devices to a computer is an example of an external interface. To implement the external interface, it needs hardware and software: a controller for the external device and a special program that manages the controller, a driver.
In any computer, the external interface is implemented through several ports, including LPT, PS/2, COM, USB, etc. (See Figure 1). Each port has its own function.
IEEE 1284 (Printer port, parallel port, LPT) - a device compatible with the international parallel interface standard intended for connection to a personal computer. The name "LTP" comes from the standard name "LTP1" (Line Printer Terminal or Line PrinTer) in the operating system of the MS DOS family. Currently, this interface is mostly compatible with the USB interface and is used to connect peripherals (scanner - printer - photocopier). But mainly used for high speed printing and printer. With this mainly Cetronics, Betronics, HP, Hewlett-Packard produced by companies. They are based on the standard 1284.3-2000 and 1284.4-2000. Working modes:
-
SPP(Standard Parallel Port) — unidirectional port, fully compatible with Cetronics interface.
-
Nibble Mode— equipped with additional devices based on two-way data exchange in SPP mode (4 bytes)
-
Byte Mode— Old controllers based on the IEEE 1284 standard are sometimes used for two-way data exchange.
-
EPP(Enhanced Parallel Port) - working device Intel, Xircom and Zenith Data Systems - two-way data exchange, at a speed of 2 Mbytes/second
-
ESR(Extended Capabilities Port) is a working device from Hewlett-Packard and Microsoft companies, in addition, it has a data compression app and works in DMA mode.
Network switch (TCP/IP port) or switch (switch, repeater) - a device designed to connect several nodes in one segment in computer systems. The main difference from concentrators is that data given to one device is transmitted to other switches through a switch. The switches work in the channel mode of the OSI model, and nodes are connected to one network through MAC addresses. Network-level routers are used to connect multiple networks.
Working with the internal ports of the computer.
The internal ports of the computer serve to ensure the communication of internal devices with each other, just like the external ports. Internal ports are also used for data (signal) transmission, and each port has a special number. Each internal device has its own port. From these ports, depending on the processor's command, it can receive or transmit information from this port. If the microprocessor gives an OUT command to a certain digital port, data can be transmitted from this port. The size of this data can be 1 or 2 bytes. If the microprocessor gives the IN command, it means that information should be read from this port.
For example, the state of pressing an optional key on the keyboard. In this case, the result is immediately visible. But this process goes through several stages. When a keyboard key is pressed, the CPU issues an IN command to the keyboard port. It detects which key was pressed and transmits it to the output ports.
A number of internal ports starting with 944 (ZV0(16)) are for black and white graphics mode, and those starting with 976(3D0(16)) are for raster graphics mode. Those starting at 1008 (3F0(16)) are used to control the floppy disk, and those at 1013 (3F5(16)) are used to write to and read from the floppy disk.
If the computer does not have external ports, then the computer can work only with the data contained in it, that is, external devices cannot be connected. This creates many difficulties. Internal ports cannot be unavailable. Because without them, it is difficult for the computer to work and not burn. Human blood vessels deliver oxygen to the human body, while ports deliver information (commands) to the computer's devices. It is clear that a person cannot live without blood vessels, and a computer is not a computer without ports.
3.An interface is a boundary between two systems, devices or programs, it is an auxiliary control circuit or a communication device that forms a link between elements.
Front end - the environment that provides communication between the user and devices:
Command line interface: a computer construction that opens the way with the help of a text line (command);
Graphical user interface (graphical user interface, GUI): A software function that presents elements of the monitor;
Dialog interface;
Single language interface: the user can "talk" to the program in his native language.
Brain interface (in English: brain-computer interface) - the computer is responsible for controlling the sound and radiation according to the changes in the user's brain with the help of electrodes and receptors installed in the brain.
Physical interface is an environment for working with physical devices. When we talk about this environment, we mainly mean computer ports:
Network interface;
Gateway (telecommunications) - a device connecting local networks with larger networks, for example, the Internet;
Shina(Computer);
COM interface (Component Object Model interface) - allows using abstract functions and features in the form of specific functions in other programs through the components of this interface;
According to the method of data exchange, the interface is divided into parallel and interfaces
4A computer network (computer network, data exchange network) is a communication system between two or more computers. Data exchange is carried out by using different physical phenomena: electrical signals or different forms of electromagnetic radiation.
The computer network, in turn, is divided into several types based on certain rules.
Classification
-
According to territorial boundaries and dimensions:
-
a) Personal network (PAN, Personal Area Network);
-
b) Local network (LAN, Local Area Network);
-
c) HomePNA;
-
d) City network (MAN, Metropolitan Area Network);
-
e) National network;
-
f) International computing network (WAN, Wide Area Network);
-
According to the network of the operating system:
-
a) based on Windows;
-
b) based on UNIX;
-
c) based on NetWare;
-
d) Mixed;
-
According to functional application:
-
a) Data storage network;
-
b) Farms with servers;
c)
-
d) SOHO network;
-
In relation to:
-
a) Client-server;
-
b) Multi-layered architecture;
-
c) Point - point;
-
d) Monochromatic (uniformity);
-
By type of network topology:
-
a) Tire;
-
b) Star;
-
c) Circle;
-
d) Grille;
-
e) Mixed topology;
-
f) Fully connected topology;
-
To ensure continuous communication if necessary:
-
a) Packet network, for example Fidonet and UUCP;
-
b) Online network, for example Internet and GSM
Protocol stack
A set of protocols of several types can be used during computer network management. Below are some of them:
ARCNET, DECnet, ethernet,IP, TCP, UDP, AppleTalk, Token ring, IPX, SPX, FDDI, HIPPI, Myrinet, QsNet, ATM IEEE 488, usb, IEEE 1394 (Firewire, iLink), X.25, frame relay, Bluetooth IEEE 802.11, Systems Network Architecture, RapidIO
Communication theory
-
Levels:
-
a) OSI model;
-
b) Practical level;
-
c) Level of information provision;
-
d) Sessional level;
-
e) Transportable level;
-
f) Network level;
-
g) Switching;
-
h) Routing;
-
i) Channel level (Data connection level);
-
j) Physical level;
-
Types of data exchange between networks:
-
a) Wired (wired) communication: PSTN telephone network, Modem and switch communication, Fixed lines (Vydelennyelinii);
-
b) Packet switching: Frame relay, PDH, Ethernet, RS-232;
-
c) Information exchange on optical fiber: Synchronous optical networking, Fiber distributed data interface;
-
d) Wireless communication
-
i) Near-radius movement: Bluetooth, Human Area Network;
-
ii) Medium radius traffic: IEEE 802.11, Netsukuku
iii) Long range movement: Satellite communication, MMDS, SMDS
-
e) Data exchange using a mobile phone: CSD, GPRS, HSCSD, EDGE, UMTS, HSDPA, HSUPA, CDMA, CDPD, Paging networks, DataTAC, Mobitex, Motient;
1.3 Tasks performed by concentrators
Network concentrator - is a network device, which mainly serves to combine several Ethernet devices in one segment. This device is connected with coaxial cable or optical fiber conductors. Currently, they are not widely used - instead of them, network switches are used in the form of a separate segment. These switches are roughly called "intellectual concentrators".
In today's modern technologies, several similar devices are used, for example, concentrator, hub, repeater. Although they are similar to each other, they differ depending on their function and structural application.
Concentrators usually consist of several ports, which are connected to separate segment cables of network nodes. Concentrators try to accommodate different local network protocols on the same segment, for example Ethernet, Token Ring. The main reason for this is the variety of different local area network protocols, for example Ethernet, Tokent Ring, FDDI and 1OOVG-AnyLAN networks.
Concentrators work in the physical environment of the OSI model of the network, transmitting the signal from one port to all active ports. If there is an input from two or more ports at the same time, a collision will occur and the data frames will be damaged. Concentrators always work in half-duplex mode.
This problem can be solved mainly by combining a large number of concentrators to eliminate the aforementioned collision.
Description of concentrators:
-
Number of ports- hubs with 4, 5, 6, 8, 16 ports (usually the last two) are usually produced and used for connecting to the network, and when several concentrators are used, the cascade method is used;
-
Data exchange speed- the data exchange speed of concentrators usually varies between 10 and 100 Mb/s. The speed is changed automatically or with the help of a switch. The advantage of concentrators is that it transmits information to all ports at the same speed;
-
Type of network transfers- usually a special conductor or optical fiber conductor, mixed transmissions are used in some concentrators. For example, by coordinating special conductors and coaxial cables;
For a specific protocol, concentrators with a special structure and functionality are sometimes used, for example, Token Ring concentrators are also called MSAU. Each concentrator performs a number of functions, and this depends on its several characteristics and which protocols it supports. Its basic function is the relative function. For example, in the Token Ring protocol, a malfunctioning port can be disconnected and retransmitted to an additional network, this is one of its unwritten classifications.
Ethernet hubs
Coaxial cables are already used to connect several physical segments in an Ethernet technology device, and the main function it performs - that is, the signal received from one port is called a "returner" with the ability to send it to all ports in the network. In networks where coaxial cable is used, dual-port repeaters are usually used to connect only two segments, and the term concentrator is not usually used in relation to it.
Using the 10 Base-T specification, parts of Ethernet networks are created, and if it is not used, only two nodes can be managed. Multiport Ethernet switches are called concentrators or hubs, and typically achieve the centralization of multi-node segments. An Ethernet hub usually has 8 to 72 ports, and most of them are for connecting cables to the network. The figure below shows a typical concentrator, which has 16 ports and is built with the 10Base-T standard and RJ-45 medium, and also has one AUI port for external transfer.
Usually a transceiver is connected to this port and it works on coaxial or fiber optic cables. With this transformer, the concentrator can be connected to the main cable, and it can be used in several concentrators, and it can be carried from the workstation to a distance of usually more than 100m.
When combining hierarchical systems with concentrators in 10Base-T technology, coaxial or optical fiber conductors are not required, it is enough to connect the last port. The RJ-45 port is designed to connect to a network adapter and is called MDI-X (cross-over MDI). The adapter is connected to the concentrator in a non-intersecting position using a standard connecting cable.
Multi-port repeater - Ethernet concentrator is used according to the four-hub rule. All large ports are associated with a single return block and are routed through two port returners and a single return through the return block. This is done only in the rule of four. But in other models, a separate return block is attached for each port.
Laser radiation can be used in single-mode optical fiber cables, and through this, information can be transmitted up to 40-100 km.
Multi-segment concentrators
It is not possible to use concentrators to connect different segments between computers, and it is not possible to establish any connection with busses on concentrators. Multi-segment concentrators are needed to split multiple segments, and this allows for easy change. (image below)
Large multi-segment concentrators, such as Nortel Networks' System 5000 or 3Com's PortSwitch concentrators, require separate software to associate a port with one of the internal buses, such as local configuration through a console port.
As a result, the administrator can connect (connect) to the user's computer in the network through any ports on the concentrator. This can then control each segment through the concentrator's structure software. If on the next day a segment is in the state of loading (peregruzka), it can contact the computer through other segments in the concentrator.
Structural application of the concentrator
Depending on the structure of the concentrators, the scope of its use differs and shows it. All workgroup concentrators are designed with a certain number of ports, corporate concentrators are modular, and departmental concentrators are flow structured. Such division is not considered important, and modular concentrators can also be used as corporate concentrators.
Methods of increasing concentrator ports
It is a very simple structural application, and this device always creates a separate case for unnecessary elements (for example, ports, indication section and supply source). Because it is useless to occupy these elements. Usually, this type of concentrator can create only one data exchange environment, and the total number of ports can be changed from 4-8 to 24. One port must be reserved for connecting to the network bus (this port works with the AUI interface). In this way, a concentrator port on an arbitrary physical environment can be practically addressed.
Connection methods
-
modular concentrators;
-
flow concentrator;
-
modular flow concentrators;
local network service
List of used literature
-
B.X., Dzhurayeva X.G., Irgashev "Informatics and information technologies" Tashkent - 2001.
-
Rakhmonkulova SI IBM "working on personal computers". T., UUI, 1994.