SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Introduction to the science of the general structure of cars. Classification of cars
Plan.
-
The purpose and task of studying science.
-
Classification of cars
-
Technical description of the car.
Automotive construction is taught as a specialty subject. In the process of studying the science, one will gain understanding about the types of cars, their structure, their classification, their work, their technical service, and the role of the car in the national economy. Also familiar with cars produced in our country.
Classification. Cars and trailers used by motor vehicles form a combined vehicle system. This system is divided into cargo-carrying and passenger-carrying parts according to its function. For cargo carriers - trucks, tractors, trailers and semi-trailers; passenger carriers - cars, buses, trailers and semi-trailers; special equipment includes specially equipped transport vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers.
Rolling stock intended for cargo transportation is divided into general and specialized groups according to the state of use. The body of trucks belonging to the general group is in the form of a four-wall (board) platform. And the body of specialized trucks is adapted only for the transportation of certain loads (dump truck, van, tanker, etc.). Trucks are divided into seven classes according to the maximum permissible mass: up to 1,2 tons; 1,3-2,0; 2,1-8,0; 9,0-14; 15-20; 21-40; Above 40 tons.
Trucks equipped with a tipping body, adapted to transport viscous (viscous) cargo, are called dump trucks, and those adapted to tow trailers or semi-trailers are called dump trucks. If a car or a tractor-car alone pulls one or more trailers, such a system of vehicles is called a car train.
Passenger cars are divided into the following categories according to the working volume of the engine cylinders: very small (up to 1,21), small (1,3-1,81), medium (1,9-3,51), large ( greater than 3,51), very large (unbounded).
Buses are passenger cars and have eight or more seats. Buses depending on their length: very small (up to 5 m), small (6,0-7,5 m), medium (8,0-9,5 m), large (10,5-12 m), very large (double) (16,5 m and longer) are divided into categories.
All types of vehicles are divided into two groups depending on the nature of traffic on different roads: vehicles with natural (normal) permeability and vehicles with high permeability. Entrants of the first group are designed for roads adapted for traffic and have one leading bridge. Those in the second group can walk even on extremely difficult roads. All wheels of these cars are steering.
To distinguish cars according to the above signs, a size called the wheel formula is used. For example: 4×2; 4×4; 6×4; 6×6 and hakosa.
Each car factory produces the basic model of the car and its modifications that differ from it in some indicators and constructions. For example: ZIL-130; Likhachev factory, model number 130.
Currently, a new system (indexing) has been put into circulation for determining rolling stock. This designation system is similar to the previous one, consisting of letters representing the name of the plant and four or five numbers. The first number represents the class of the car, the second the type of the car, the third and fourth the model number, and the fifth (if placed) the serial number of the modification.
The second number allows you to divide cars according to their function or specialization: 1- light cars; 2-buses; 3-trucks; 4-saddle-shaped shakers; 5- dump trucks; 6-cisterns; 7-vans; 8th reserve (reserve); 9 special cars. The system of marking cars by the first two numbers has the following general appearance:
Trucks |
|||||||
The highest (maximum) permissible mass, t |
1,2 |
1,3-2 |
2,1-8 |
9-14 |
15-20 |
21-40 |
40 |
Automobile index; on-board platform |
13 |
23 |
33 |
43 |
53 |
63 |
73 |
Shatakchi |
14 |
24 |
34 |
44 |
54 |
64 |
74 |
Dump truck |
15 |
25 |
35 |
45 |
55 |
65 |
75 |
Cars |
|||||||
Working volume of the engine, l. |
1,2 |
1,3-1,8 |
1,9-3 |
3,5 |
|||
index |
11 |
21 |
31 |
41 |
|||
Buses |
|||||||
Length, m |
5 |
6-7,5 |
8-9,5 |
10,5-12,0 |
16,5 |
||
index |
22 |
32 |
42 |
52 |
62 |
||
Examples: Kamsk automobile plant board car, maximum permissible mass 15184 kg, twentieth model - KamAZ-5320; The working volume of the passenger car engine of the Gorky Automobile Plant is 2,445 l, the second model is GAZ-3102; Bus of the Pavlov plant, length 7,15 m, first model-PAZ-3201.
Technical description of the car. The manual attached to the car by the factory provides information on its technical description. These data will consist of the following main indicators: nominal load capacity expressed in tons (kg) or number of seats; maximum permissible mass expressed in tons (kg); gauge dimensions expressed in m (mm); engine type and model; maximum speed with full load (km/s); Fuel consumption per 100 km (l).
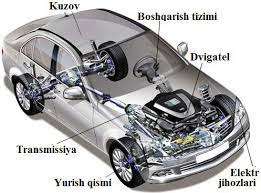
In addition to the mentioned indicators, the technical description includes the engine and its system, transmission, wheels and suspensions, control system, electrical equipment, cabin, body, additional equipment, fuel tank (tank) size and adjustment and brief information on control is also provided.
A brief technical description of some basic cars.
Indicators |
Car model (copy) |
|||
GAZ-24 |
PAZ-3201 |
ZIL-130 |
KamAZ-5320 |
|
Carrying capacity or number of seats |
5-6 |
26 |
6 t |
8 t |
Maximum permissible mass, kg |
1820 |
7155 |
9525 |
15184 |
Engine type |
Carburetor |
Carburetor |
Carburetor |
Dizel |
Engine model |
ZMZ-24 |
ZMZ-672 |
ZIL-130 |
KamAZ-740 |
The number and arrangement of cylinders |
4, row |
8, V-shaped |
||
Working volume of cylinders, l |
2,445 |
4,25 |
6,0 |
10,85 |
The maximum effective power of the engine, KW (ok) |
70 (95) |
84,6 (115) |
110 (150) |
154,4 (210) |
The maximum speed of the car, km/h |
145 |
80 |
90 |
85 |
Basic phrases: tractor, trailer and semi-trailer, platform, tipper, van, tanker, road train, spreader, maximum mass, working volume of cylinders, number of seats, length, formula of wheels, technical description.
CONTROL QUESTIONS
-
Tell the purpose and task of studying science.
-
List the classification of trucks
-
Classify cars.
-
Explain the technical description of the car.