SHARE WITH FRIENDS:
Archimedes' law and its application
technological map of the subject
Goals and objectives:
Educational: Teaching students Archimedes' law and its use.
Educational: Education in the spirit of confidence in chance. Educating children in the spirit of saving water and not polluting.
Developer: Forming a scientific outlook.
Teaching materials and equipment : Physics textbook and multimedia textbook. Computer. CD disk. Forming students' concepts about water in teaching physics. (Guide for teachers.) E. Turdikulov. M. Musayeva. Tashkent-2007. Educational film "Archimedes' law and its application" 13 minutes. Necessary equipment for demonstration-experiment. Blackboard, chalk.
Demonstration experiences: An experiment demonstrating Archimedes' law (Textbook 38-39).
Basic concepts and terms: lifting force; pressure inside the liquid; Archimedes' law; Conditions of floating bodies; ships, balloons, oil tankers.
Darsniug block diagram
Course stages |
Time |
|
1. |
Organizational part |
|
2. |
Holding experiments-demonstrations |
|
3. |
Open the content of a new topic. Show a movie |
|
4. |
Strengthen the theme |
|
5. |
Home assignments |
|
Content of the lesson:
There are two ways to teach Archimedes' law to students. Conducting experiments and issuing laws based on the results. The second way is to make a law in theory, and then see the confirmation in experience. The second way is more difficult for students. Therefore, it is better to choose a middle way: to explain in a theoretical way, showing a partial experience.
At the beginning of the lesson, the pressure exerted by the liquid on the bottom of the container is repeated. After that, the legend of "Archimedes and the crown" is remembered, and the task set before him is given to the students. Then an object that sinks in the liquid is attached to a dynamometer and its weight is measured. Then the body is lowered into the water and the dynamometer reading is recorded again. These experiments are presented in the textbook. In this way, after each experiment, students are asked questions and their answers are obtained. In order to show the dependence of the lifting force on the volume, if possible, an experiment is conducted with bodies of the same weight, but of different volume.
Demonstrate Archimedes' law
Required tools: 1) Archimedes bucket; 2) Universal tripod;
3) Containers made of polypropylene; 4) Base.
A disk-shaped pointer is attached to the end of the spring fixed to the iron frame. Depending on its position, the stretching of the spring is observed. A sliding arrow is placed in front of the pointer to indicate one or another of its positions.
Procedure for demonstration of experience:
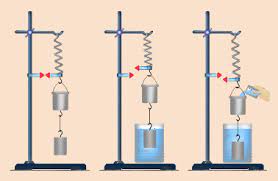
1) First, it is shown that the capacity of the bucket is exactly equal to the volume of the cylindrical object, for this purpose, it is shown by lowering the object into the bucket 1-2 times. Attention is paid to the fact that there are no gaps between them and that they occupy the entire volume of the container.
The dynamometer is attached to the handle of the tripod and a bucket and a cylindrical body are hung on it (Fig. a). In this case, the indication of the dynamometer is determined by a disk pointer.
2) Then a container of water is placed under the cylindrical body and the body is submerged in water. A base is placed under the container (Fig. b).
-
a) b) c)
In this case, the disk pointer will move up. Students are then told that the upward force exerted by the liquid on the bucket is equal to the weight of the additional load placed on the bucket and object.
3) To determine the magnitude of the upward pushing force, take the second water glass and slowly pour the water in it into the bucket (Fig. v). When the object and the bucket go down and the bucket is filled with water, the disk indicator shows the previous position. So, it is explained to the students that the weight of the water in the bucket is equal to the amount of force that lifts the body up by the liquid. The volume of water in the bucket is equal to the volume of the body immersed in the liquid.
An experiment can be carried out in normal and salt water to show that it depends on the type of liquid. Finally, Archimedes' law and Archimedes' force FA=ρVthe bodyg After that, this force is calculated theoretically. Derivation is given in the textbook. The conditions of floating objects, the application of Archimedes' law by the means of flying balloons in the air will be explained. Then the film will be shown.
Before the film is shown, the students will be asked some questions to activate the students. Students should answer them after watching the film;
-
to explain to the students the phenomenon seen in the film, to distinguish experiences and examples not shown in the lesson, to draw pictures or drawings on them, to make calculations.
In order to strengthen the lesson, the problem is solved.
Masala. The size is 20 cm3 What is the buoyant force acting on a body when it is immersed in water?
B eri 1 gan : Formula : Solution:
V = 20 cm3=210-5 m3
ρ = 1000 kg / m3 FA= rVg FA= 1000 kg / m3
g=10m/s2 210-5 m310m/s 2 = 0,2N
Must find
FA=?
After that, the creation, structure and principle of operation of balloons
an understanding is given. It explains why balloons now work with continuously heated air.
Questions for conclusion:
-
The definition of Archimedes' law refers to a body immersed in a liquid or gas. Does the law apply if part of the body's volume is submerged?
-
The balloon rises due to the Archimedean force acting on it. Will it completely disappear from the atmosphere?